Differential vs. Single-ended Measurements
A differential voltage is “floating”, meaning that it has no reference to ground. The measurement is taken as the voltage difference between the two wires. The main benefit of a differential measurement is noise rejection, because the noise is added to both wires and can then be filtered out by the common mode rejection of the data acquisition system. Differential measurements should be used if the sensor is in a noisy environment or for sensors with output voltages susceptible to noise interference. For example, we recommend that the thermopile output from Apogee SI-100 series infrared radiometers should always be measured differentially because the small voltages are susceptible to noise.
A single-ended measurement is taken as the voltage difference between a wire and ground. The noise is only on the positive wire, and as a result, it is still measured along with the output voltage from the sensor. Some sensors, for example amplified versions of Apogee SP and SQ series sensors, only have a single output and must be wired into a single-ended channel. A sensor with a differential output can be wired for single-ended by wiring the low side to ground. This is usually done to reduce the number of channels needed to measure the sensors. It should be noted that some sensors (for example, the thermopile output from Apogee SI-100 series infrared radiometers) can output a negative voltage which means that the data acquisition system needs to be able to measure negative voltages.
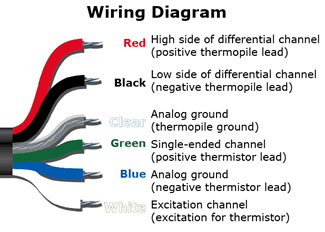
Wiring diagram for SI series infrared radiometer.
It should also be noted that taking a single-ended vs. differential measurement might also be based on the data acquisition system or the cabling. Shielded twisted-pair cable is also very effective at reducing noise in the signal other types of cable might not have the same effect. The data acquisition system is also important to consider if it doesn’t have a very uniform ground the signal could be biased. In most cases, modern data acquisition systems have improved in this area and it isn’t as much of a concern.
It should be stated that differential measurements should always be used if there are enough available datalogger channels or if the data acquisition system cannot measure negative voltages. Table 1 (below) shows which measurement method should be used with specific Apogee Instruments sensors. Again, it should be remembered that any in the differential measurement column can be measured single-ended if the conditions warrant it.
Table 1: Apogee Instruments Sensors Output
| Differential | Single-ended |
|---|---|
| SI-100 Series - thermopile (single-ended measurement strongly discouraged) |
SI-100 Series - sensor body temperautre |
| SP-100 Series | SP-200 Series |
| SO-100/200 Series | SF-110 |
| SQ-100/300 Series | SQ-200 Series |
| SU-100 | ST-100 |
